Union-find
Contents
Union-find¶
Union-find also called disjoint-set is a data structure capable of tracking and merging of disjoint-sets. It is important an used in many other algorithms such as Kruskal’s algorithm, Prolog unification etc.
There are two additional speed improvements to the algorithm:
rank (weighing) is a new parameter initialized with 0 for all elements. With the union the ranks are matched and the parents nodes get +1.
path compression, flattens the tree structure whenever find is performed.
More information in this from the University of Princeton
Solution¶
The algorithm implements two functions
union(a, b)- merge A’s set with B’s setfind(a)- finds what set A belongs to
Imports¶
import numpy as np
from bokeh.plotting import figure, show, output_notebook
Algorithm¶
class UnionFind:
"""Implementation of the Union-find algorithm to handle disjoint-datasets
"""
def __init__(self: UnionFind, size: int):
"""initialise UnionFind object. Mainly setup rank and parent lists
Args:
self (UnionFind): pointer to itself
size (int): number of unique elements in the tree / disjoint dataset
"""
self.rank = [0 for i in range(size)]
self.parent = [-1 for i in range(size)]
def find(self: UnionFind, x: int):
"""find root of a given elements
Args:
self (UnionFind): pointer to itself
x (int): elements to locate
Returns:
int: root element of tree containing the element x
"""
parent = self.parent[x]
while parent >= 0: # termination condition has changed
x = parent
parent = self.parent[x]
return x
def union(self: UnionFind, x: int, y: int):
"""create tree by merging subtree where x belongs to subtree where y belongs to
Args:
self (UnionFind): pointer to itself
x (int): element/subtree to merge
y (int): element/subtree to merge
"""
# find root of the subtrees (if there are any)
root_x = self.find(x)
root_y = self.find(y)
# if they don't belong to the same subtree, the have to be merged
if root_x != root_y:
if self.rank[root_x] >= self.rank[root_y]:
self.parent[root_x] += self.parent[root_y] #parent[root_id] is always negative
self.parent[root_y] = root_x
self.rank[root_x] = max(self.rank[root_y] + 1, self.rank[root_x])
else:
self.parent[root_y] += self.parent[root_x]
self.parent[root_x] = root_y
self.rank[root_y] = max(self.rank[root_x] + 1, self.rank[root_y])
def same(self: UnionFind, x: int, y: int):
"""[summary]
Args:
self (UnionFind): pointer to itself
x (int): [description]
y (int): [description]
Returns:
[type]: [description]
"""
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
def findRootAndSize(self: UnionFind):
"""Returns root element and the unique element number
Args:
self (UnionFind): pointer to itself
Returns:
list: list of tuple for (root element, number of elements in subtree)
"""
return [(idx, -val) for idx, val in enumerate(self.parent) if val<0 ]
Test¶
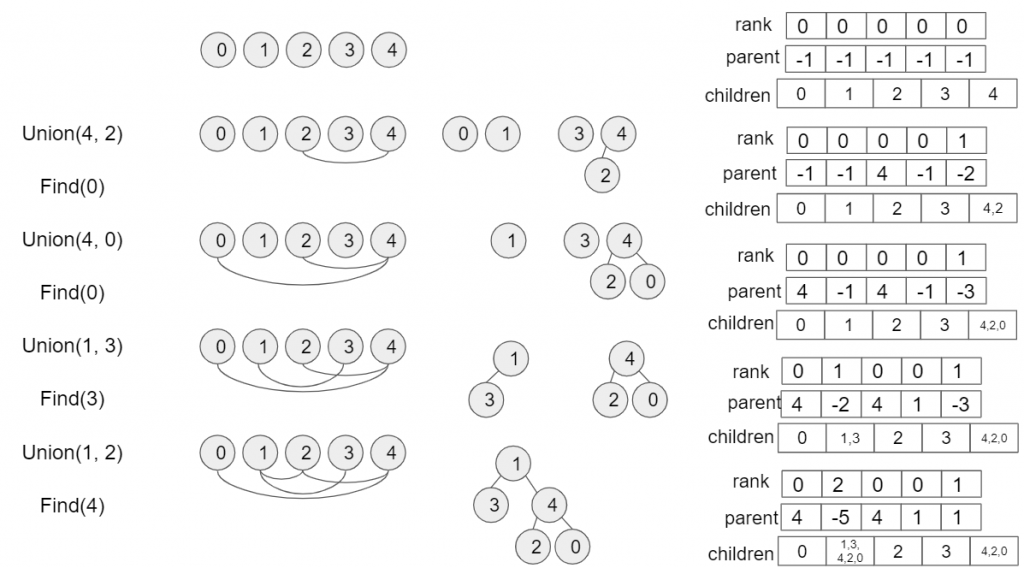
print("Create disjoint dataset of 5 unique elements")
unionfind = UnionFind(5)
print(" + Merge(4,2)")
unionfind.union(4, 2)
print(" - Root(0)={}".format(unionfind.find(0)))
print(" + Merge(4,2)")
unionfind.union(4, 0)
print(" - Root(0)={}".format(unionfind.find(0)))
print(" + Merge(4,2)")
unionfind.union(1, 3)
print(" - Root(3)={}".format(unionfind.find(3)))
print("There are {} subtrees with [(root/nbrOfElements), ...]: {}".format(len(unionfind.findRootAndSize()), unionfind.findRootAndSize()))
print(" + Merge(4,2)")
unionfind.union(1, 2)
print(" - Root(4)={}".format(unionfind.find(4)))
print("There are {} subtrees with [(root/nbrOfElements), ...]: {}".format(len(unionfind.findRootAndSize()), unionfind.findRootAndSize()))
Create disjoint dataset of 5 unique elements
+ Merge(4,2)
- Root(0)=0
+ Merge(4,2)
- Root(0)=4
+ Merge(4,2)
- Root(3)=1
There are 2 subtrees with [(root/nbrOfElements), ...]: [(1, 2), (4, 3)]
+ Merge(4,2)
- Root(4)=1
There are 1 subtrees with [(root/nbrOfElements), ...]: [(1, 5)]