Maze Solver with Lee’s Algorithm
Contents
Maze Solver with Lee’s Algorithm¶
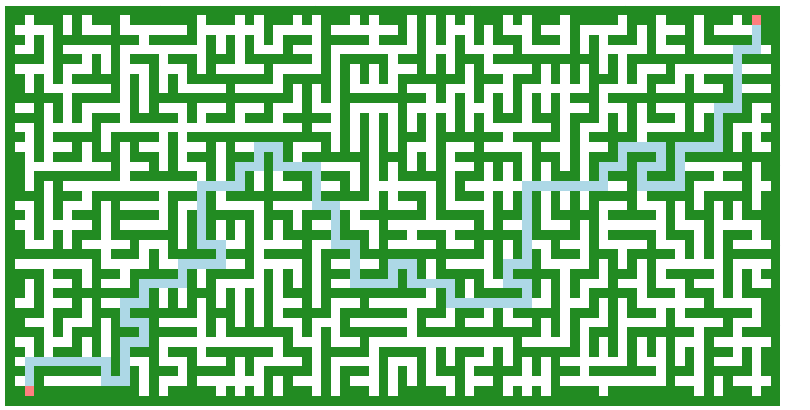
Fig. 18 Lee’s Maze Solution¶
Lee’s Algorithm give always an optimal solution based on a bread-first-search and queues. It requires considerable amount of memory and is slow.
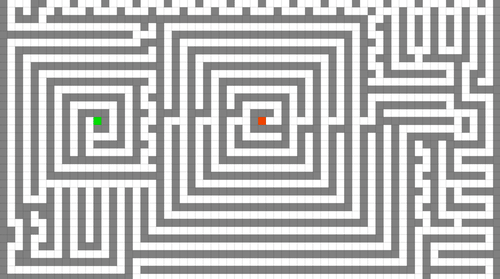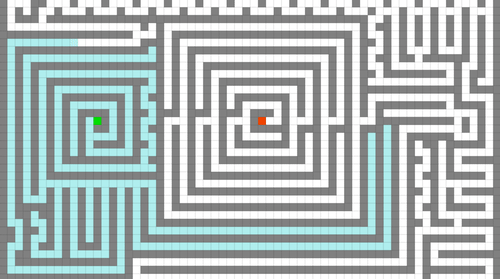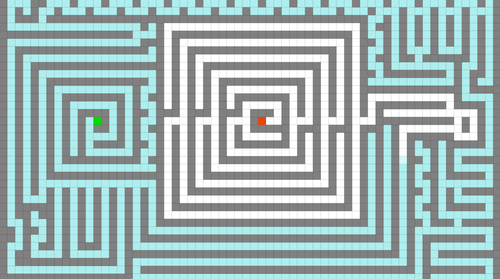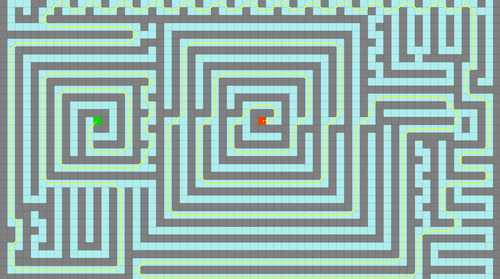
Fig. 19 Lee’s Algorithms Demo Source: @richardfunkygifs¶
Solution¶
Create an empty queue to store the coordinates of the matrix and initialize it with the source cell having a distance of 0 from the source, marking it as visited.
Starting from the source cell, call the BFS procedure.
Initialize a boolean array of the same size as input matrix and all values set to false. This is used to store the visited status of a coordinate.
Run a loop till the queue is empty
Dequeue front cell from the queue
Return if the destination cell is reached
Otherwise, For each of the four adjacent cells of a current cell, if the cell value is 1 and they are un-visited, enqueue the cells and mark them as visited.
If all queue elements are processed and destination is not reached, return false.
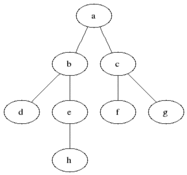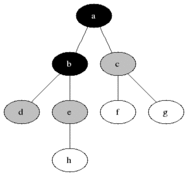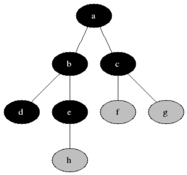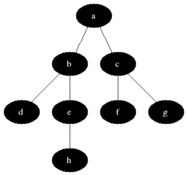
Fig. 20 Bread First Search Example Source: Wikipedia¶
Imports¶
from collections import deque
from IPython.display import clear_output
# generate maze from other notebook
# Run 008-maze-generation-kruskal notebook
%run 008-maze-generation-kruskal.ipynb
Algorithm¶
def bfsLee(maze, src: list, dest: list):
"""Function to find the shortest path between source cell and destination cell.
Args:
maze (list): 2 dimensional maze matrix
src (list): y-x coordinates of source cell
dest (list): y-x coordinates of destination cell
Returns:
list: [list of the maze solution path, distance of the solution]
"""
# These arrays show the 4 possible movement from a cell
rowNum = [-1, 0, 0, 1]
colNum = [0, -1, 1, 0]
# Solution path, list of [y,x] coordinates
solution = []
# Checking if source and destination cell have value 1
if maze[src[0]][src[1]]!=1 or maze[dest[0]][dest[1]]!=1:
return None, -1
# get maze size
maze_rows = len(maze)
maze_cols = len(maze[0])
# list of visited cells
visited = [[False for i in range(maze_cols)]
for j in range(maze_rows)]
# Mark the source cell as visited
visited[src[0]][src[1]] = True
# Create a queue for BFS
queue = deque()
# node [[coordinates], distance]
# Distance of source cell is 0
node = [src,0]
solution.append(node)
# enqueue src node
queue.append(node)
# distance
# Perform BFS starting from source cell
while queue:
cur = queue.popleft() # Dequeue the front cell
# If we have reached the destination cell, return the final distance
pt = cur[0]
if pt[0] == dest[0] and pt[1] == dest[1]:
return solution, cur[1]
# Otherwise enqueue its adjacent cells with value 1
for i in range(4):
row = pt[0] + rowNum[i]
col = pt[1] + colNum[i]
# Enqueue valid adjacent cell that is not visited
if (((row >= 0) and (row < maze_rows) and (col >= 0) and (col < maze_cols)) and
maze[row][col] == 1 and
not visited[row][col]):
visited[row][col] = True
adjcell = [[row,col], cur[1]+1]
solution.append(adjcell)
queue.append(adjcell)
# Return -1 if destination cannot be reached
return None, -1
def checkAdjacent(point_1: list, point_2: list):
"""Check of
Args:
point_1 (list): y,x coordinates of first point
point_2 (list): y,x coordinates of second point
Returns:
bool: true if cell is adjacent
"""
# These arrays show the 4 possible movement from a cell
_rowNum = [-1, 0, 0, 1]
_colNum = [0, -1, 1, 0]
_adjacent = False
for i in range(len(_rowNum)):
if point_1[0] == point_2[0]+_rowNum[i] and point_1[1] == point_2[1]+_colNum[i]:
_adjacent = True
return _adjacent
def getSolution(src: list, dst: list, solution: list):
"""Get shortest solution path
Args:
src (list): y,x coordinates of the startpoint
solution (list): array of points of the solution and their distance to the src-point
Returns:
list: optimum solution path
"""
_solution_path = []
# get maximum distance
_distance = None
_prev_cell = None
for i in range(len(solution)-1, 0, -1):
if not _distance and not _prev_cell:
if solution[i][0] == dst: # found destination point start pathsearch
_distance = solution[i][1] - 1
_prev_cell = solution[i][0]
else:
if _distance == solution[i][1] and checkAdjacent(solution[i][0], _prev_cell): # if correct distance and if adjacent cell
_solution_path.append(solution[i][0])
_distance -= 1
_prev_cell = solution[i][0]
return _solution_path
def drawSolution(maze: list, src: list, dst: list, solutionpath: list):
"""draw the start- and endpoint as well as the solution
0 = wall
1 = cell
2 = path
3 = start- endpoint
Args:
maze (list): 2 dimensional array of the maze
src (list): y,x coordinates of the startpoint
dst (list): y,x coordinates of the endpoint
solutionpath (list): array of points of the solution
Returns:
list: 2d array of the maze including solution
"""
maze_tmp = maze.copy()
# draw solution
for point in solutionpath:
maze_tmp[point[0]][point[1]] = 2
# draw start and endpoint
maze_tmp[src[0]][src[1]] = 3
maze_tmp[dst[0]][dst[1]] = 3
return maze_tmp
def findEmptyCell(maze: list, corner: int):
"""find empty cell in cell starting at a corner
Args:
maze (list): maze to search through
corner (int): where to start (0=bottomleft, 1=topleft, 2=topright, 3=bottomright)
Returns:
list: row,col coordinates of the first empty cell
"""
maze_rows = len(maze)
maze_cols = len(maze[0])
if corner == 0:
range_rows = range(0, maze_rows-1, 1)
range_cols = range(0, maze_cols-1, 1)
elif corner == 1:
range_rows = range(0, maze_rows-1, 1)
range_cols = range(maze_cols-1, 0, -1)
elif corner == 2:
range_rows = range(maze_rows-1, 0, -1)
range_cols = range(maze_cols-1, 0, -1)
else:
range_rows = range(maze_rows-1, 0, -1)
range_cols = range(0, maze_cols-1, 1)
# find empty cell
for row in range_rows:
for col in range_cols:
if maze[row][col] == 1: # valid cell found
return [row, col]
Test¶
no_solution = True
while no_solution:
# generate maze with function from 008 notebook
size = {'x': 80, 'y': 40}
maze = generateMaze(size['x'], size['y'])
maze = createBorder(maze)
# get maze size
maze_rows = len(maze)
maze_cols = len(maze[0])
# find empty cell in topleft corner
src = findEmptyCell(maze, 0)
# find empty cell in bottomright corner
dst = findEmptyCell(maze, 2)
print("Maze Size : {}x{}".format(maze_cols, maze_rows))
print("Source Cell is : {}".format(src))
print("Destination Cell is : {}".format(dst))
# execute lees algorithms
(solution, dist) = bfsLee(maze, src, dst)
# draw points and solution
if dist != -1:
no_solution = False
path = getSolution(src, dst, solution)
print("Length of the Shortest Path is", dist)
maze_solved = drawSolution(maze, src, dst, path)
else:
#no_solution = False##
print("No solution exists")
clear_output(wait=True)
Maze Size : 81x41
Source Cell is : [1, 2]
Destination Cell is : [39, 78]
Length of the Shortest Path is 178
output_notebook()
plot = figure(x_range=(0, 1), y_range=(0, 1),
plot_height=maze_rows*10, plot_width=maze_cols*10)
plot.axis.visible = False
plot.outline_line_color = '#ffffff'
plot.image([maze_solved], x=0, y=0, dw=1, dh=1, palette=['#228b22', '#ffffff', '#add8e6', '#ff7f7f'])
show(plot)