Morse Code
Morse code was invented by Samuel Finley Breese Morse (1791--1872). The code consists of a sequence of Dots and Dashes. There are a couple of rules to follow:
- The length of a dot is one unit
- A dash is three units
- The space between parts of the same letter is one units
- The space between letters is three units
- The space between words os seven units
Morse Code is encoded as follows:
It can be decoded with the help of the decoding tree
Number of possible codes:
| Number of Dots and Dashes | Number of Codes |
|---|---|
| \(1\) | \(2^1=2\) |
| \(2\) | \(2^2=4\) |
| \(3\) | \(2^3=8\) |
| \(4\) | \(2^4=16\) |
| \(5\) | \(2^5=32\) |
| \(6\) | \(2^6=64\) |
| \(7\) | \(2^7=128\) |
| \(8\) | \(2^8=256\) |
| \(9\) | \(2^9=512\) |
| \(10\) | \(2^{10}=1024\) |
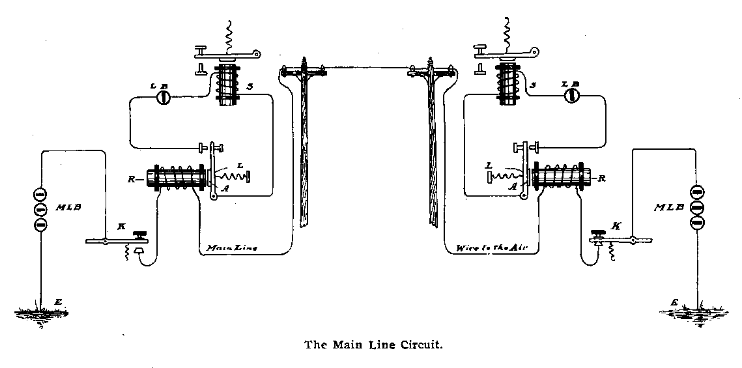
Telegraph
The most famous application of the morse code is for the telegraph communication. Over one wire a non-simultaneous bi-directional communication can be established.