VNC Remote Control
VNC is a protocol to let you connect and view the screen of your remote controlled PC. But this isn't very secure and should not be enabled over the internet but only locally. VNC is often used to hack Linux PC. Therefore you should use VNC over SSH where the data is encrypted and very secure.
x11vnc
Perfect fast and configurable solution for almost all Linux distributions. x11vnc does not create an extra display (or X desktop) for remote control. Instead, it uses the existing X11 display shown on the monitor of a Unix-like computer in real time.
Install
sudo apt-get install x11vnc
Config
Generate password file
x11vnc -storepasswd
Enter VNC password:
Verify VNC password:
The password in now store by default in the file ~/.vnc/passwd
Start
x11vnc -usepw -forever -display :0 -safer -bg -o /home/user/Documents/log/vnc/x11vnc.log -localhost
-forever: listen forever to input connections-display :<nbr>: Define display to use-usepw: uses password file stored in~/.vnc/passwd-safer: don't allows remote comands-noremoteand-novncconnect-localhost: allows only local connections works only local or over SSH-o logfile: defines location of the logfile-bg: Launches in Background
Autostart
In Lubuntu with LXDE add the following line to the file: /etc/xdg/lxsession/Lubuntu/autostart
@x11vnc -usepw -forever -display :0 -safer -bg -o /home/user/Documents/log/vnc/x11vnc.log -localhost
In Lubuntu with lightdm add the following line to the file: /etc/xdg/lxsession/Lubuntu/autostart
@x11vnc -usepw -forever -safer -bg -o /home/user/Documents/log/vnc/x11vnc.log -localhost -auth /var/run/lightdm/root/:0 -display :0
In Gnome add the following line to the file: /etc/gdm/Init/Default
x11vnc -usepw -forever -display :0 -safer -bg -o /home/zas/Documents/log/vnc/x11vnc.log -localhost
VNC over SSH
Linux
Open SSH Tunnel
ssh -N -T -L 5900:localhost:5900 <hostname>
This forwards our local port 5900 to the host computers port 5900, just replace 5900 with the port you normally use for VNC connections, i.e if you use display 20 then it would read ssh -N -T -L 5920:<hostname>:5920. The middle part is the hostname hostmachine, replace with the correct number for your network. The -L is the local port forward option while the -N option prevents a shell from opening so we cannot execute commands and the -T option disables pseudo-tty allocation.
Launch VNC Viewer in Linux
vncviewer localhost:5900
Windows
To connect to VNC over SSH in Linux you need a VNC Viewer like UltraVNC and Putty
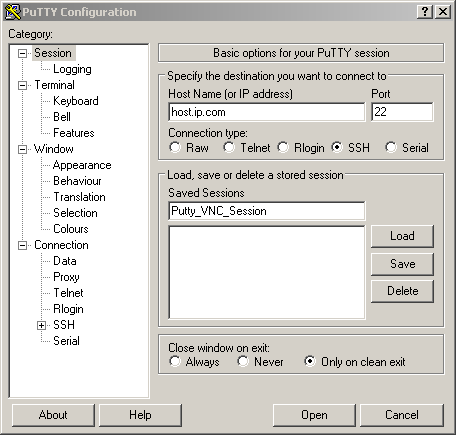
Putty Config
see: Putty-VNC
Start VNC
- Start Putty with the above configuration
- Enter password
- Open a VNC Viewer
- Connect to
127.0.0.1
Troubleshooting
If you have problems connecting to the remote machine, and if the connection gets rejected then you should quit your local VNC Server. Because you are connecting via localhost he might respond to your request.
Macintosh
Install Tools
Tightvnc is a great vncviewer and is installable through Homebrew, as well as Putty:
sudo port install tightvnc
sudo port install putty
Set up SSH Tunnel
Terminal
ssh -p <portnumber> -L 5900:127.0.0.1:5900 <hostname>
Putty
see: Putty-VNC
Launch VNC Viewer in Mac
vncviewer localhost:5900
or use the program "Chicken Of VNC"
Putty
- Create a new putty session
- goto Session -> Add hostname and port
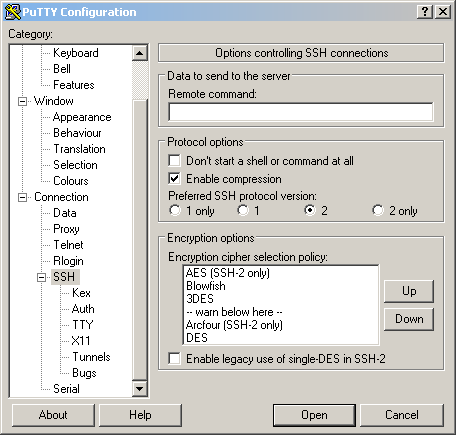
- goto SSH -> Enable compression
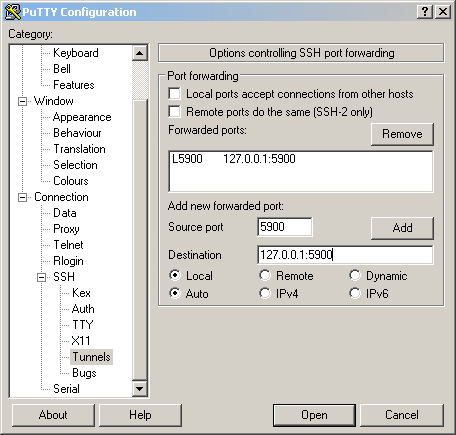
- goto SSH -> Tunnels -> Add tunnel
- Source Port:
5900 - Destination :
127.0.0.1:5900 - Click Add